How to Install and Configure Podman on Redhat 8
Installation and Configuration of Podman/Docker on Redhat 8/CentOS 8
Container normally work on single process, when container
run the process start and container stop working the process of container will
stop, but process have multiple process inside it. Redhat have prebuilt runtime
Universal Base Image (UBI) that is use for containers for save storage and
network utilization when multiple application use same base image. Universal
Base Image (UBI) RPM similar to red hat rpm but have limited number of rpms and
their updates because UBI is a subset of Red Hat Enterprise Linux. When
Universal Base Image (UBI) run on red hat enterprise Linux (RHEL) the repository
of RHEL is automatically enable for UBI.
Traditionally System Administrators manage disk image,
virtual machines to reduce operational
overhead, increase automation, improve reliability and increase security on an
organization While Containers have improved the deployment, development, and
maintenance of applications. Containers provide isolation and simplicity to
manage IT.
As per developer mind set when he develop a containerized
application, his/her focus on running a handful of container. Prebuilt
container images are available (java, python, PHP etc.), developer choose the
container image base on container image size or focus on database not an
operating system.
Traditional the application is available in package format
(.rpm, .deb,.tar, etc.) and its update due to vulnerabilities, the OS and
application availability is the responsibility of system owner (system
administrator and developer), but in container base application developer have
all the responsibility from operating system to application code because
developer choose the runtime environment for the application. That is the
reason container provide appliance or VM image easily. In Container Base Image
system administrator is responsible for Linux kernel, container engine and its
dependencies. Once the container image created it will update or change by
rebuild it to pick up the updated base image layer.
UBI is redistributable subset of Red Hat Enterprise Linux
(RHEL) for building container-based software, the only difference is the terms
and conditions. UBI is use in highly secure environment like financial sectors,
government bodies, banking etc. Universal Base Image (UBI) is the good choice
for free software projects. UBI package updates are available as similar to
RHEL packages through repository but red hat rebuild UBI in every 6 month if
rpm updates already available. The Linux container are portable in an environment
therefore is no compatibility issue as in past and Linux container is also a
lightweight because host kernel is share to the containers that run on the
system. Important thing is about linux container that not every Linux container
can run on any linux kernel version.
Note: UBI 8 fully compatible on RHEL 8 and commercially
reasonable support on RHEL 7. UBI 7 fully compatible on RHEL 7 and support
workload specific on RHEL 8.
Redhat support OCI (Open Container Initiative) client container
tool (Docker) like podman, buildah and skopeo. Redhat 8 is not support Docker
and in redhat 7 some early Docker packages are available but from redhat 7.5
since 2018 Docker is not available. In Redhat you can perform the most of the
operation of Docker by install the compatible tool for Docker CLI command with
podman, the tool is "podman-docker".
Docker and podman are similar container tool if you are
experience to work on any one tool you can work on other tool just replace
docker with podman or podman with docker on command.
Here we are working podman that is similar container tool of Redhat open container tool. In Redhat Linux 3 main command line tool of container that we first discuss below.
Podman: The fundamental tool to run a container that is
almost similar to docker is podman. Podman is a container engine that manage
Open container initiative and container images on Linux machines. Non-root user
also run container without daemon. Podman also support images format of docker
images. Podman is an open source tool that available on most of the Linux
operating systems. Container of podman also known as pod, the concept of pod is
similar to the concept in kubernetes. In podman libpod library is use to allow
code share with other tools.
Buildah: This tool is use to build container images. Buildah
can also use for existing docker files.
Skopeo: A tool is use for working with container images and
registries. This tool is use for transferring container images and image
repositories. Skopeo libraries is use for inspecting, signing and manipulating
containers. Skopeo is also use to change container images format of Open
container initiative (OCI) and docker to other.
Three more tool that are use in Redhat containerization
environment.
Udica: This tool is use for generate SELinux policies for
container. Udica is create tailored security policy to control container how
much access system resources (storage, device and networks), this is called
hardening of container.
CRIU: CRIU stands for Checkpoint and restore containers in
userspace. CRIU provide faster restart time after restore the running container
from checkpoint on disk. CRIU also restore the container on another host system
that is stateful container migration.
CRI-O: This is a lightweight container runtime for
Kubernetes. Container Runtime Interface (CRI) is an Open container initiative
(OCI) compatible that is light weight alternative for docker to kubernetes
environment.
To install the container tools fast stream for latest stable
versions of Podman, Buildah and Skopeo, type the below mention command. This
container tool update 4 times in a year.
yum module install container-tools:rhel8
For stable stream container tools type the below mention
command. This container tool update 1 times in a year and only update security and
bug fixes.
yum module install container-tools:2.0
To use the docker command (docker CLI) by use of podman and
buildah tool, need to be install package “podman-docker”. To install the
package “podman-docker”, type the below mention command.
yum install podman-docker -y
To install the podman and buildah that is use to run
container and create container image respectively, type the below mention
command. Here tool “cockpit-podman” is web based system management tool that is
used to manage podman containers and images.
yum install podman cockpit-podman buildah
To install the tool “Skopeo” that is use for working with
container images and registries, type the below mention command.
yum install skopeo.x86_64 -y
After install the podman packages start and enable service
“podman”, type the below mention command.
systemctl start podmansystemctl enable podmansystemctl start --user podmansystemctl enable --user podman
you also need to install cockpit tool to manage podman
container web base, type the below mention command.
yum install cockpit.x86_64 -y
After successful installation of cockpit, enable cockpit
socket, type the below mention command.
systemctl enable --now cockpit.socket
To access web base management for podman container, type the
below mention url on web browser. Then provide the access credentials.
https://10.0.81.94:9090/
To list the running sockets, type the below mention command.
systemctl list-socketssystemctl list-sockets | grep cockpit
To check the podman images through bash shell, type the
below mention command.
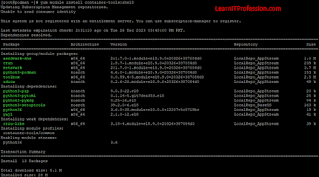
podman images
To remove the images from local machine, type the below
mention command. Use option “-f” to force removal of images from the local
machine. Images can be specified by the name or uuid, here we are removing the
images from local machine by use of UUID.
podman rmi [-f] <<image>:<tag>podman rmi [-f] a354659655
Redhat have a certified container image (Universal Base
Image “UBI”) that have lightweight and self-contained software for deployment
of applications. Here we are pull two base images (Builder images) first one is
“Apache 2.4 with PHP 8.0” and the second one is “Ruby 2.5”. To pull the
Universal Base Image (UBI) that is use as a base image for container, type the
below mention command on RHEL 8/CentOS 8.
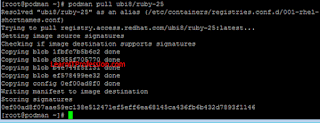
podman pull ubi9/php-80podman pull ubi8/ruby-25
After pull the image successfully from repository
“registry.access.redhat.com” verify it by type the below mention command.
podman images
Working with Image “Apache 2.4 with PHP 8.0”:
This Universal Base Image 9 (UBI 9) of Apache 2.4 with PHP
8.0 available use as a container base image for deploy applications and framework
base on PHP 8. By use of docker file build a PHP container image with an
application is an easy way. The base builder image (Apache 2.4 with PHP 8.0)
already pull by use of command “podman pull ubi9/php-80” as mention
above.
To get the application source code from github type the
below mention command, you can provide your application after modification.
Here command “git” is use to pull the code, first install git (yum install
git).
git clone https://github.com/sclorg/cakephp-ex.git app-src-php
To prepare an application in a container, put an application
source code “app-src-php” in any directory Where Docker file should be
available. Here we are creating a docker file must have name “Dockerfile” with
below mention code in a clone application directory “app-src-php”.
vi Dockerfile
Add the below mention code in file "Dockerfile".
FROM ubi9/php-80# Add application sourcesADD app-src-php .# Install the dependenciesRUN TEMPFILE=$(mktemp) && \curl -o "$TEMPFILE" "https://getcomposer.org/installer" && \php <"$TEMPFILE" && \./composer.phar install --no-interaction --no-ansi --optimize-autoloader# Run script uses standard ways to configure the PHP application# and execs httpd -D FOREGROUND at the end# See more in <version>/s2i/bin/run in this repository.# Shortly what the run script does: The httpd daemon and php needs to be# configured, so this script prepares the configuration based on the container# Parameters (e.g. available memory) and puts the configuration files into# the appropriate places.# This can obviously be done differently, and in that case, the final CMD# should be set to "CMD httpd -D FOREGROUND" instead.CMD /usr/libexec/s2i/run
To Build a new image with a docker file that we have created above, type the below mention command. In command dot “.” is use to find Dockerfile in the current directory.
podman build -t cakephp-app .
To verify the new image
“cakephp-app” has successfully created on localhost repository, type the below
mention command.
podman images
To run the resulting image “cakephp-app”
with the final application that we have build in above step, type the below
mention command. The application “cakephp-app” used the base image
“ubi9/php-80”.
podman run -d cakephp-appor for security implication to opens container port 8080 and maps it to the same port on the Host.podman run -dp 192.168.10.224:8080:8080 cakephp-app
To open application on a web browser, use below mention Uniform Resource Locator
“URL”.http://192.168.10.224:8080
To list the running container in the local machine, type the
below mention command.
podman ps -a
To enter in the bash shell of container, type the below
mention command.
podman exec -it <CONTAINER_ID> /bin/bash
Working with Image “Ruby 2.5”:
To build and running a ruby 2.5 application and framework,
ruby 2.5 is available as a base container image. The base builder image (Ruby
2.5) already pull by use of command “podman pull ubi8/ruby-25” as
mention above. To clone the application code from github to “app-src-ruby”,
type the below mention command.
git clone https://github.com/sclorg/rails-ex.git app-src-ruby
vi Dockerfile
Type the below mention code on file "Dockerfile".
FROM ubi8/ruby-25USER 0ADD app-src-ruby ./RUN bundle install --path ./bundleCMD bundle exec "rackup -P /tmp/rack.pid --host 192.168.10.224 --port 8081"
To build a new image from above created Dockerfile, type the
below mention command. In Command dot “.” is use to find Dockerfile in the
current directory.
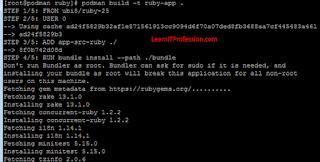
podman build -t ruby-app .
To verify the image “ruby-app” has successfully created by
use the certified base image “ubi8/ruby-25”, type the below mention command.
podman images
To run the above created new image “ruby-app”, type the
below mention command.
podman run -d ruby-apporpodman run -dp 192.168.10.224:8081:8081 ruby-app
To start the container, type the below mention command.
podman start <Names>To stop the container, type the below mention command.
podman stop <Names>To check the port of container, type the below mention command.
podman port <Names>To export a container filesystem into a tar file, type the below mention command. This compress package contain a complete directory structure.
To import a tar file and saves it as a filesystem image “abc” with a tag “latest”, type the below mention command.podman export -o <output_filename> <container>podman export <Names> > abc.tar
To verify the image has successfully created, type the below mention command.podman import <tar_filename>podman import abc.tar abc:latest
podman imagesTo remove container type the below mention command. To forcefully remove use option “-f”, remove associated volume “-v” and remove specified link use option “-l”.
podman rm <OPTIONS> <Container ID>podman rm <OPTIONS> <Container Name>podman rm 22453b452f50
Thanks for Read This Article






Comments
Post a Comment