How Create and Delete GPT Partition with LVM on CentOS Linux 8
Create and Delete GPT Partition with GDisk on Centos Linux 8
In this article we will create and delete GPT Partition (File System) on Vmware work station environment on CentOS 8 Linux operating system. GPT stands for GUID partition table, GUID is a global unique identifier. The purpose of this lab is that we cannot create partition size more then 2TB using fdisk, therefore to resolve this issue we need GNU parted command with GPT. GNU is a free software tool and it belong to the family of Linux operating system. You must know that EFI uses GPT where BIOS uses a Master Boot Record. GPT that is GUID partition table is gradually replacing MBR (Master Boot Record). By default Redhat Enterprise Linux / CentOS comes with GPT kernel support.
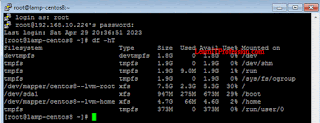
To check the current file systems (partitions) on CentOS linux 8 operating system, type the below mention command.
df -hT
To check the version of CentOS 8 Linux operating system, use command "cat" to view the complete text of file.
cat /etc/redhat-release
To verify package "gdisk" is install or not, type the below mention command on CentOS 8 Linux operating system.
dnf list gdisk
To install package "gdisk" on CentOS 8 Linux operating system, type the below mention command.
dnf install gdisk
The package "gdisk" on CentOS 8 Linux operating system has successfully installed, please have a look below given image.
To check all the physical drives and its associated file systems (LVM and fixed size partitions), type the below mention command.
lsblk
Here we are create and delete new file system "backup" with a size of 2GB for this lab environment. First we need to add 2GB hard drive, this is virtualization environment therefore 2GB hard drive is add with this VMware workstation virtual machine.
To check this newly added hard drive inside CentOS Linux 8 operating system, type the below mention command. The virtual hard drive is showing on CentOS Linux 8 operating system with the name of "sdb".
lsblk
Create GPT Partition:
To create the partition on newly added virtual hard disk on CentOS/RedHat Linux 7/8 operating system type the below mention command. Here we create only single partition "/dev/sdb1" and assign a complete size "2GB" to this partition.
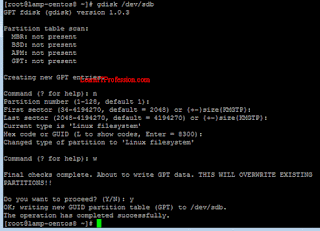
gdisk /dev/sdb
then provide the below mention given details.
Command (? for help): n
Command (? for help): w
Do you want to proceed? (Y/N): Y
For command "n" means new partition, on partition number (1-128, default 1) just press enter, first sector (press enter), last sector (press enter), Hex code (press enter), w for write and y for proceed.
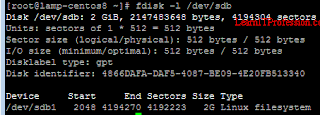
To check the partition "/dev/sdb1" has been successfully created, type the below mention command.
gdisk -l /dev/sdb
By use of command "gdisk" it is not showing that is "/dev/sdb1" but we can use command "fdisk" better representation to list the partitions.
fdisk -l /dev/sdb
To create the physical volume of this partition "/dev/sdb1", type the below mention command.
pvcreate /dev/sdb1
To create a volume group "backup" of this physical volume "/dev/sdb1", type the below mention command.
vgcreate backup /dev/sdb1
To verify volume group "backup" has been successfully created, type the below mention command.
vgs
To create a logical volume "backup" of complete size of volume group "backup", type the below mention command.
lvcreate -l 100%FREE -n logical-volume volume-grouplvcreate -l 100%FREE -n backup backup
Create a mount point backup "backup" to mount this logical volume "backup" by use of command "mkdir".
mkdir /backup
and to verify the directory "backup" with it's permission, use command "ls -lrd".
ls -lrd /backup
To create a new file system with .xfs extension, type the below mention command.
mkfs.xfs /dev/volume-group/logical-volumemkfs.xfs /dev/backup/backup
mount /dev/volume-group/logical-volume /mount-pointmount /dev/backup/backup /backup
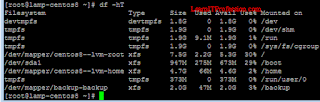
To verify logical volume has been successfully mounted, use command df -hT.
df -hT
For permanent entry edit the file "fstab" by use of editor "vi".
vi /etc/fstab
Add the below mention line for permanent mount of logical volume "backup".
/dev/mapper/new_vol_group-newlogicalvolume /mount-point xfs defaults 0 0
/dev/mapper/backup-backup /backup xfs defaults 0 0
Delete GPT Partition:
To delete the GPT partition first dismount the logical volume "backup" by use of command "umount".
umount /backup
rm -rf /backup
Then remove the logical volume "backup" by use of command "lvremove".
lvremove /dev/Volume-Group/Logical-Volume
lvremove /dev/backup/backup
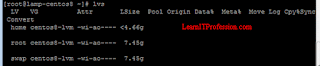
To verify logical volume "backup" has been successfully remove, type the below mention command.
lvs
vgremove backup
To verify the volume group "backup" has been successfully removed, type the below mention command.
vgs
To check the /dev/sdb1 (origin) is completely free now, type the below mention command.
pvs -o+pv_used
Now it's time to remove hard drive partition "/dev/sdb1" by use of command "gdisk", but first remove its lable by use of command "pvremove"
pvremove /dev/sdb1
Then remove hard drive partition "/dev/sdb1"
gdisk /dev/sdb
provide below mention details to remove the hard drive partition "/dev/sdb1".
Command (? for help): d
Command (? for help): w
Do you want to proceed? (Y/N): y
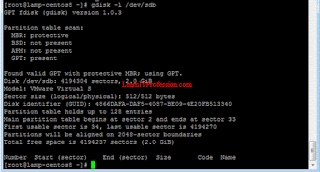
To verify the partition "/dev/sdb1" has been completely remove, type the below mention command/
gdisk -l /dev/sdb
Remove the mount point entry from file "fstab", otherwise it will create issues when machine reboot.
vi /etc/fstab
/dev/mapper/backup-backup /backup xfs defaults 0 0
Power off the CentOS/Redhat 7/8 linux operating system for remove the hard drive from virtual machine.
init 0
Finally remove the hard drive of size 2GB from the Virtual Machine setting area after power off the virtual machine.
This is the complete process of Create and Delete GPT Partition with LVM on CentOS/Redhat Linux 7/8.
Thanks for read this Article















Comments
Post a Comment